
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of the content on the web page.
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render the web page. For example,
My web page Hello, world!
This is my first web page.
It contains a main heading and paragraph .
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body . The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title , and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p .
Let's see the meaning of the various elements used in the above example.
: contains the paragraphs of text on the web page
elements, they are used to mark text as important and emphasized respectively
Note: Only the elements inside the tag renders in the web browser.
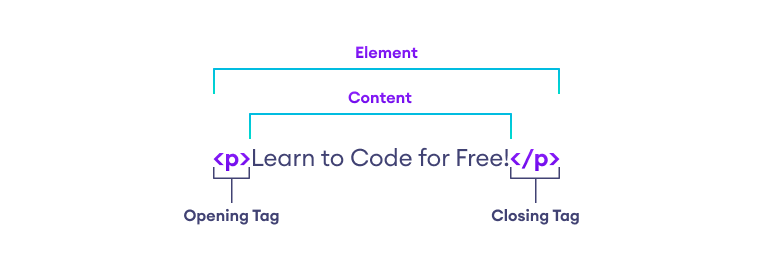
HTML elements consist of several parts, including the opening and closing tags, the content, and the attributes. Here is an explanation of each of these parts:
HTML elements can have attributes, which provide additional information about the element. They are specified in the opening tag of the element and take the form of name-value pairs. Let's see an example:
http://example.com"> Example The href is an attribute. It provides the link information about the tag. In the above example,
Note: HTML attributes are mostly optional.
We need to follow a strict syntax guidelines to write valid HTML code. This includes the use of tags, elements, and attributes, as well as the correct use of indentation and white space. Here are some key points about HTML syntax:
1. HTML tags consist of the element name, wrapped in angle brackets. For example, ,
, are some HTML tags.
2. HTML elements are created by enclosing the content of the element inside the opening and closing tags of the element. For example,
Some text.is an HTML element.
3. HTML attributes are used to provide additional information about HTML elements and are specified in the opening tag of the element. For example,
www.google.com">Click Here Here, target is an attribute.
4. HTML code should be well-formed and properly indented, with each element on its own line and each level of hierarchy indented by one level. This makes the code easier to read and understand, and can help to avoid errors. For example,
My First HTML Page My First HTML Page
Hello World!